VERBS: What is a Verb? Useful Rules, Types & Examples
English Verbs!!! What is a verb? Learn verb definition and different types of verbs in English with useful verbs list. Learn verb examples and grammar rules with ESL printable worksheets.
What Is A Verb?
What is a verb? A verb is a word or group of words that describes an action, experience or expresses a state of being.
Verbs are the main part of a sentence and one of the nine parts of speech in English.

Verb examples: Walk, is, seem, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, …
- He speaks English
- I don’t know how to spell the word
- She studies hard
There are many different types of verbs in English grammar: irregular verb, modal verb, dynamic verb, stative verb, auxiliary verb, causative verb,…
Types of Verbs & Verb Examples
Learn different types of verbs in English with useful grammar rules and verb examples.
Irregular Verbs
Irregular Verb Definition
Irregular verbs are common verbs in English that do not follow the simple system of adding “d” or “ed” to the end of the word to form the past tense (the past simple and/or the past participle).
Irregular Verb Examples
- Fall – fell – fallen
- Feed – fed – fed
- Feel – felt – felt
- Fight – fought – fought
- Find – found – found
- Fly – flew – flown
- Forbid – forbade – forbidden
- Forget – forgot – forgotten
- Forgive – forgave – forgiven
- Freeze – froze – frozen
- Get – got – got
- Give – gave – given
- Go – went – gone
- Grind – ground – ground
- Grow – grew – grown
- Hang – hung – hung
- Have – had – had
- Hear – heard – heard
- Hide – hid – hidden
- Hit – hit – hit
- Hold – held – held
- Hurt – hurt – hurt
- Keep – kept – kept
- Kneel – knelt – knelt
- Know – knew – known
- Lay – laid – laid
- Lead – led – led
- Lean – leant/ leaned – leant/ leaned
- Learn – learnt/ learned – learnt/ learned
- Leave – left – left
- Lent – lent – lent
- Lie (in bed) – lay – lain
- Lie (not to tell the truth) – lied – lied
- Light – lit/ lighted – lit/ lighted
- Lose – lost – lost
- Make – made – made
- Mean – meant – meant
- Meet – met – met
- Overtake – overtook – overtaken
- Pay – paid – paid
- Put – put – put
- Read – read – read
- Ride – rode – ridden
- Ring – rang – rung
- Rise – rose – risen
- Run – ran – run
- Saw – sawed – sawn/ sawed
- Say – said – said
- See – sawed – seen
- Sell – sold – sold
- Send – sent – sent
- Set – set – set
- Sew – sewed – sewn/ sewed
- Shake – shook – shaken
- Shed – shed – shed
- Shine – shone – shone
- Shoot – shot – shot
- Show – showed – shown
- Shrink – shrank – shrunk
- Shut – shut – shut
- Sing – sang – sung
- Sink – sank – sunk
- Sit – sat – sat
- Sleep – slept – slept
- Slide – slid – slid
- Smell – smelt – smelt
- Sow – sowed – sown/ sowed
- Speak – spoke – spoken
- Spell – spelt/ spelled spelt/ spelled
- Spend – spent – spent
- Spill – spilt/ spilled – spilt/ spilled
- Spit – spat – spat
- Spread – spread – spread
- Stand – stood – stood
- Steal – stole – stolen
- Stick – stuck – stuck
- Sting – stung – stung
- Stink – stank – stunk
- Strike – struck – struck
- Swear – swore – sworn
- Sweep – swept – swept
- Swell – swelled – swollen/ swelled
- Swim – swam – swum
- Swing – swung – swung
- …
Common Irregular Verbs List in English

Modal Verbs
Modal Verb Definition
Modal verbs are a small class of auxiliary verbs used to express possibility, obligation, advice, permission, ability, …
Modal Verb Examples
- Will
- Shall
- Would
- Should
- Ought to
- Must
- Mustn’t
- May
- Might
- Can
- Could
- Have to/ Has to
- Don’t/ Doesn’t have to
Modal Verb Examples

Modal Verbs To Express Ability
Learn how to use Modals of Ability in English
- Be able to
- Can/Can’t
- Be able to
- Could/Couldn’t
- Managed to
- Be able to
- Can/can’t
Modals of Ability Image

Modals for Asking Permissions
Learn useful Modals for Asking Permissions in English
- Can
- Could
- May
- Would
Modals for Asking Permissions Image

Perfect Infinitive with Modals
The structure “have + past participle” is called a perfect infinitive.
Learn how to use perfect infinitive with modal verbs in English: must have, can’t have, should have, shouldn’t have, needn’t have, ought to have, may have, might have, could have, would have.
Perfect Infinitive with Modals Image

Infinitives
What is a To-Infinitive?
A to-infinitive is a verbal consisting of to + a verb, and it acts like a subject, direct object, subject complement, adjective, or adverb in a sentence.
We use the infinitive:
- To indicate the purpose of an action
- As subject of the sentence
- As direct object of the sentence
- As subject complement
- As an adjective
- As an adverb
- After adjective
- After object that is noun or pronoun referring to a person
- Used with question word
Verbs Followed by Infinitives
List of commonly used Verbs Followed by Infinitives
- Attempt
- Ask
- Arrange
- Beg
- Begin
- Care
- Choose
- Claim
- Consent
- Continue
- Dare
- Decide
- Demand
- Deserve
- Dislike
- Expect
- Fail
- Forget
- Get
- Hesitate
- Hope
- Hurry
- Intend
- Learn
- Like
- Love
- Manage
- Mean
- Neglect
- Need
- Offer
- Plan
- Prefer
- Prepare
- Pretend
- Proceed
- Promise
- Propose
- Refuse
- Remember
- Seem
- Start
- Stop
- Struggle
- Swear
- Threaten
- Try
Zero Infinitive
We use the Zero Infinitive when:
- After modal auxiliary verbs
- After the object after certain verbs, such as hear, see, make, let
- After verbal idioms would rather and had better
- Used with WHY
Zero Infinitive in English

Gerunds
What is a Gerund?
Gerunds are verbals that function as nouns and have an –ing ending.
The gerund form of verbs is used as follows:
- Used as subject of a sentence
- Used as direct object of a sentence
- Used as a subject complement
- Used as an object of a preposition
- Used after certain expressions
How to Use Gerunds in English

Verbs Followed by Gerunds
Useful list of Verbs Followed by Gerunds in English.
- Admit
- Advise
- Anticipate
- Acknowledge
- Appreciate
- Avoid
- Bear
- Begin
- Complete
- Consider
- Defer
- Delay
- Deny
- Discuss
- Dislike
- Enjoy
- Entail
- Finish
- Forget
- Hate
- Intend
- Involve
- Justify
- Keep
- Like
- Love
- Mention
- Mind
- Miss
- Postpone
- Practice
- Prefer
- Quit
- Recall
- Recollect
- Recommend
- Regret
- Resent
- Resist
- Risk
- Sanction
- Start
- Stop
- Suggest
- Tolerate
- Try
List of Common Verbs Followed by Gerunds



Present and Past Participles
What is a Participle?
A participle is a verbal that is used as an adjective and most often ends in -ing or -ed. They function as adjectives, thus participles modify nouns or pronouns.
Types of Participles
There are two participles in the English language: the present and past participle.
The Present Participle Image

The Past Participle Image

Finite and Non-finite Verbs
Learn Finite and Non-Finite Verb Forms in English.
Finite Verb Forms
A finite verb is controlled by the number of the subject. If the subject is singular, the verb is singular. If the subject is plural, the verb is plural.
Examples:
- They arestudying reproduction in shellfish.
- I sing with the university chorus.
Non-finite Verb Forms
A non-finite verb is not controlled by the number, person and tense of the subject.
Examples:
- I don’ t want to go home in the dark.
- She put a blanket over the sleeping child.
Finite and Non-finite Verb Forms

Dynamic Verbs
Dynamic Verb Definition
A dynamic verb is a verb that shows continued or progressive action on the part of the subject. This is the opposite of a stative verb.
Dynamic Verb Examples
- Eat
- Walk
- Learn
- Grow
- Sleep
- Talk
- Write
- Run
- Read
- Go
Stative Verbs
Stative Verb Definition
Stative verbs are verbs that express a state rather than an action. They usually relate to thoughts, emotions, relationships, senses, states of being and measurements.
Stative Verb Examples
Mental State
- Suppose
- Recognise
- Forget
- Remember
- Imagine
- Mean
- Agree
- Disagree
- Deny
- Promise
- Satisfy
- Realise
- Appear
- Astonish
Possession
- Have
- Own
- Possess
- Lack
- Consist
- Involve
Emotions
- Like
- Dislike
- Hate
- Adore
- Prefer
- Care for
- Mind
- Want
- Need
- Desire
Measure, cost, others
- Measure
- Weigh
- Owe
- Seem
- Fit
- Depend
- Matter
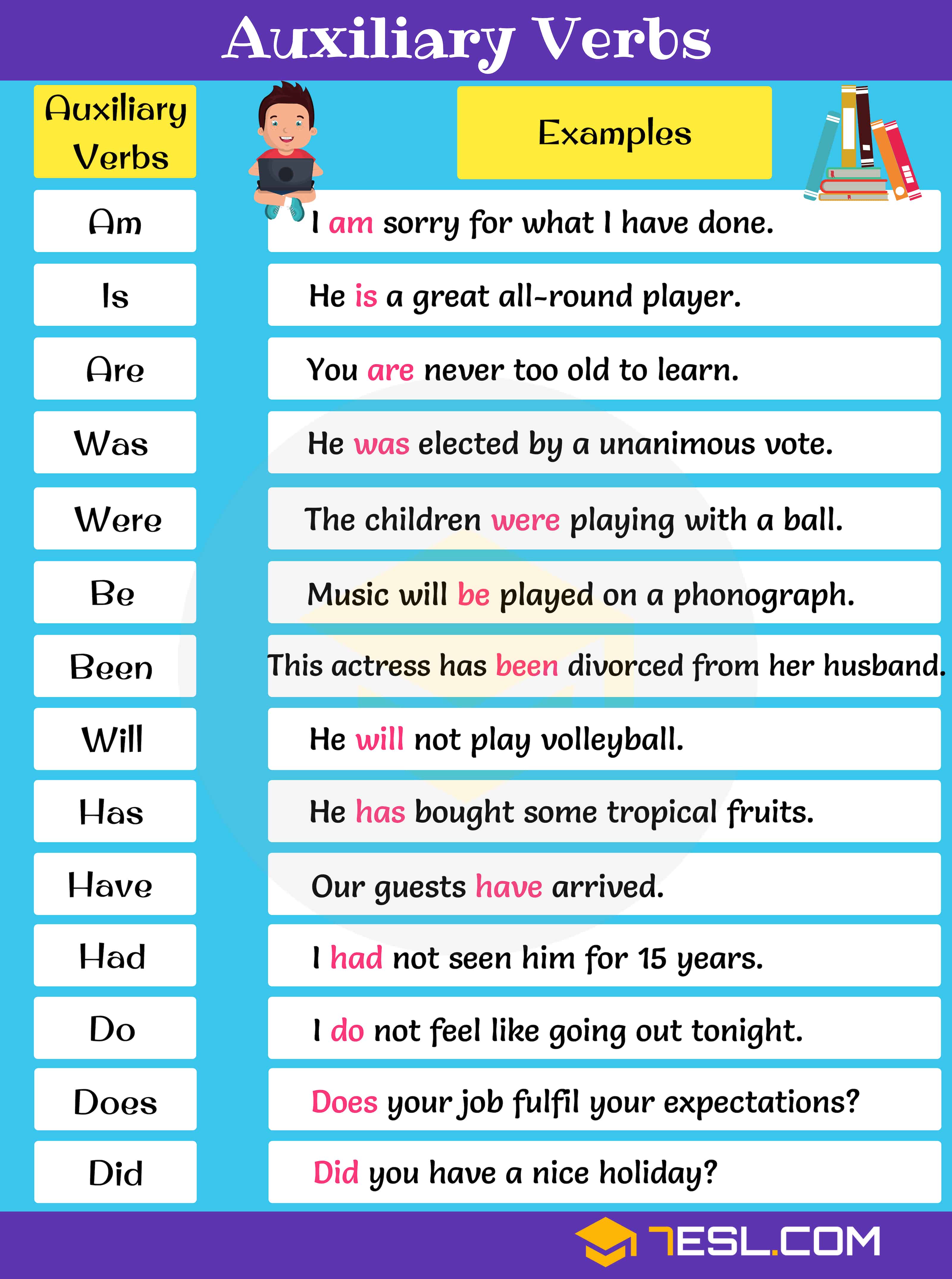
Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary Verb Definition
An auxiliary verb is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it appears, such as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. An auxiliary verb is most generally understood as a verb that “helps” another verb by adding grammatical information to it.
Auxiliary Verb Examples
- Do: I do not feel like going out tonight.
- Have: I have just received his reply.
- Be: A model railway mart will beheld on Friday.
- Will: He will not play volleyball.
Auxiliary Verb Examples
Causative Verbs
Causative Verb Definition
Causative verbs are verbs that show the reason that something happened. They do not indicate something the subject did for themselves, but something the subject got someone or something else to do for them.
Causative Verb Examples
- Have: I had the mechanic check the brakes.
- Get: I couldn’t get the engine to start.
- Make: I like him because he makes me laugh.
- Let: If you accept, please let me know.
 Causative Verb Examples
Causative Verb ExamplesSubject Verb Agreement Rules
Learn 10 Subject Verb Agreement Rules in English Grammar.
- The subject and verb must agree in number. A singular subject takes a singular verb, whereas a plural subject takes a plural verb.
- The subject is separated from the verb by “with”, “as well as”, “together with”, “along with”. These words and phrases are not part of the subject. The verb agrees with the subject.
- Two subjects joined by “and” are plural.
- Two subjects joined by “or/not”, “either…or/neither…nor”, “not only…but also” take the verb that agrees with the subject closest to it.
- With collective nouns, the verb might be singular or plural (UK), depending on meaning.
- In sentences beginning with “here” or “there“, the true subject follows the verb.
- The verb is singular if the subject is a singular indefinite pronoun. The verb is plural if the subject is a plural indefinite pronoun. And, some indefinite pronouns (some, any, all, most) may be either singular or plural, depending upon their use in a sentence.
- Use a singular verb for expressions of measurement, time. money and weight when the amount is considered one unit.
- Plural form subjects with a singular meaning take a singular verb.
- Titles of single entities are always singular.
10 Subject Verb Agreement Rules in English

List of Verbs: Examples & Images
Learn an extensive list of commonly used verbs in English.
- Do: I don’t know.
- Doubt: I doubt if it’ll snow.
- Drag: I had to drag him out of bed.
- Drive: He drives a truck.
- Drop: I dropped my sandwich.
- Dry: Raisins are dried grapes.
- Earn: He earns three times more than me.
- Eat: You can’t eat your cake and have it.
- Encourage: John encouraged Mary to learn how to speak French.
- Engage: We used to be engaged.
- Enter: He entered the room.
- Establish: The school was established in 1650.
- Examine: The doctor examined the patients.
- Experiment: They’re experimenting with a new car.
- Explore: He explored the Amazon jungle.
- Extend: We extended a hearty welcome to them.
- Fly: Tom wishes he could fly.
- Fold: Tom and Mary folded up the flag.
- Follow: We must follow the rules of the game.
- Forbid: I forbid you to smoke.
- Fry: She fried fish in salad oil.
- Generate: This machine generates electricity.
- Get: We’ve got to get the economy under control or it will literally eat us up.
- Give: The waiter gives me the menu.
- Grow: Apples grow on trees.
- Hang: Don’t you hang up on me.
- Happen: You made it happen.
- Hesitate: I hesitate to spend so much money on clothes.
- Hide: I’m hiding from Tim.
- Hug: I really need a hug.
- Hurry: It had to hurry to find a home because I was already on to something else.
- Hurt: I hurt my elbow.
- Identify: She identified him as the murderer.
- Improve: I need to improve my French.
- Include: Tom’s lunch includes a sandwich and an apple.
- Incorporate: Her business was incorporated.
- Indicate: The arrow indicates the way to go.
- Involve: This procedure involves testing each sample twice.
- Iron: I iron my clothes almost every day.
- Jog: I make it a rule to jog every morning.
- Jump: Can you jump over the river?
- Kiss: Did you kiss anybody?
- Kneel: Do not run, stand, kneel or spin in the slide.
- Laugh: Tom is laughing.
- Lay: He laid on his back.
- Learn: Children learn to creep ere they can go.
- Leave: Leave me alone!
- Lift: He couldn’t lift the table and no more could I.
- …






No comments